
Brodie Generational Capital Partners, LLC Announces Acquisition of Sur-Seal, LLC, a Leading Advanced Materials Converting Platform. Radnor, PA and Charlotte,...
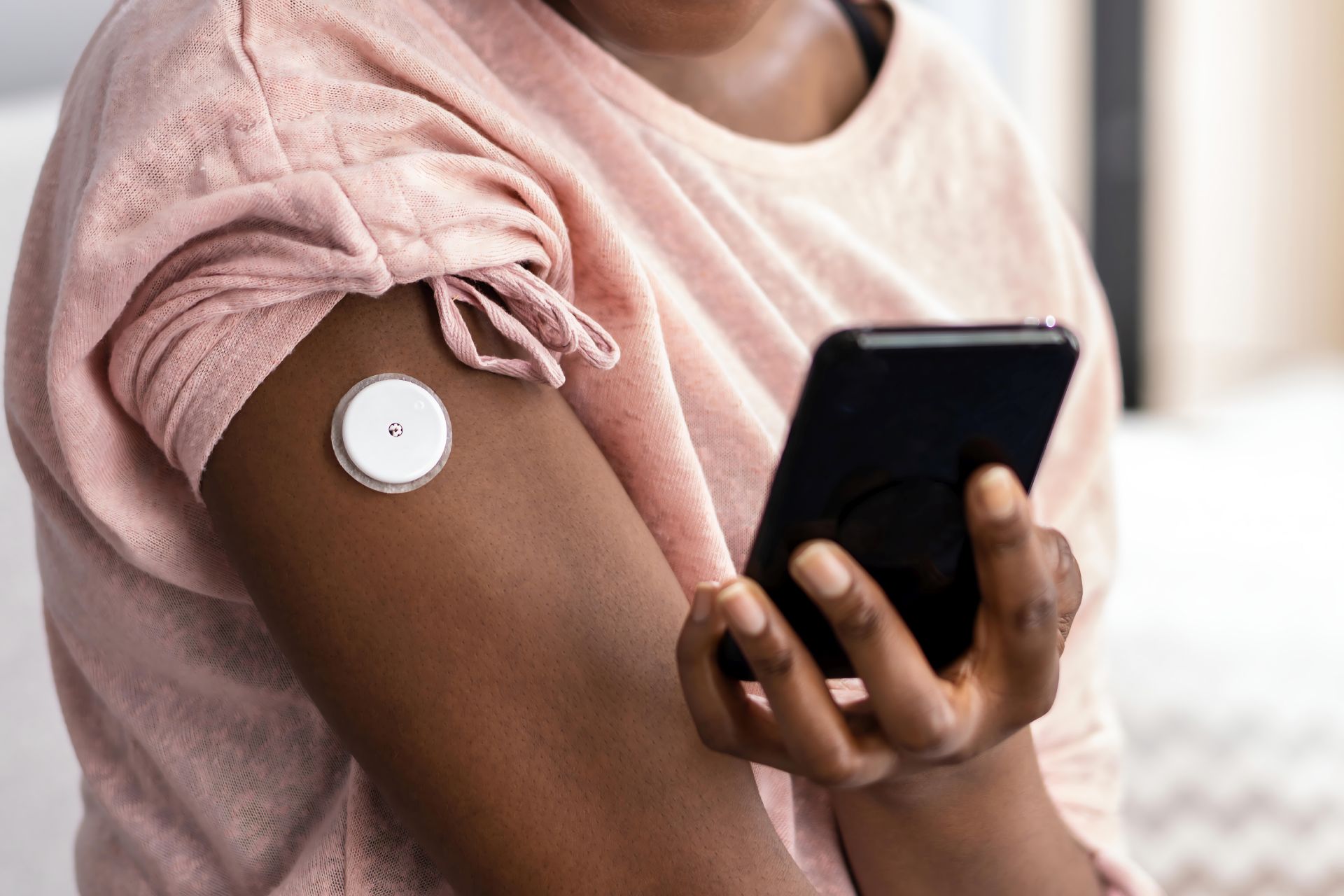
When it comes to medical device design, adhesives are fundamental. They determine whether a device can perform reliably, comfortably and safely against the skin. Biocompatible adhesives are engineered to maintain secure attachment while minimizing irritation, enabling devices to function effectively over extended wear times.
From glucose monitors and wearable sensors to wound dressings and ostomy pouches, adhesives are the quiet workhorses that hold everything together. This month, we’re taking a closer look at five of the most widely used categories: acrylics, silicones, hydrocolloids, hydrogels and rubber-based adhesives.
Adhesives that come into contact with skin must pass rigorous testing to ensure they do not cause harm. Biocompatibility means the adhesive can be worn safely without causing reactions such as rashes, itching or burns. At the same time, adhesives must strike a balance—strong enough to hold through sweat, movement and temperature changes, yet gentle enough to remove without damaging skin.
That balance plays out differently depending on the chemistry:
Acrylic adhesives are known for their durability and strong bonding properties. They adhere well to both skin and device surfaces, making them ideal for long-term applications such as wearable monitors or extended-wear patches.
Key strengths include:
Like EMI shielding materials, acrylic adhesives must perform under stress—whether that means keeping a sensor in place or blocking interference. But when strength and durability are too much for sensitive skin, silicone adhesives provide a gentler option.
Silicone adhesives are valued for their soft, gentle bond. They are easy to reposition and remove, making them the preferred choice for:
Much like thermal pads protect electronic components by absorbing stress, silicone adhesives protect skin from trauma while still providing dependable attachment. Compared to acrylics, which focus on durability, silicones stand out for their gentle, repositionable nature.
Together, they demonstrate how adhesives balance strength and skin-friendliness. But in some applications, the goal extends beyond attachment to creating a healing environment—and that’s where hydrocolloids come in.
Hydrocolloids combine adhesion with therapeutic benefits. Made from gel-forming agents like pectin or gelatin, they not only keep devices in place but also interact with the skin. Hydrocolloids can:
Because of these properties, hydrocolloids are widely used in wound dressings and ostomy care, where secure adhesion and comfort are both critical. While silicones focus on skin-friendliness, hydrocolloids add healing support, making them ideal for therapeutic applications.
Hydrogels are water-rich adhesives that provide cooling relief and gentle adhesion. They are especially useful for:
Their high water content not only cools but also conducts, making hydrogels essential in therapeutic and diagnostic applications. By emphasizing cooling and conductivity, hydrogels complement hydrocolloids and highlight how biocompatibility continues to drive innovation.
Rubber-based adhesives formulations offer high initial tack and flexibility, making them ideal for quick-adhesion needs where immediate stickiness is favored over long-term durability. Rubber-based adhesives are often used in medical applications that require conformability and fast bonding—such as bandages, wearable health monitors and drug-delivery patches—where flexibility and movement are key. They are especially useful for:
While they provide excellent immediate adhesion and comfort, rubber-based adhesives tend to have moderate resistance to heat and moisture and are best suited for short-term use. Compared to acrylics, which offer long-term durability and environmental resistance, rubber-based adhesives prioritize flexibility and fast bonding.
Biocompatible adhesives play a critical role across industries, each with unique needs:
In every case, adhesives must do more than just stick—they must balance comfort, durability and functionality. This demand for dual performance is shaping current applications and future innovations.
As healthcare moves toward personalization and home-based care, adhesives must evolve to meet new expectations. Development is focused on:
At Sur-Seal, we collaborate with leading suppliers to help manufacturers select the right adhesives for their devices. Whether strength, sensitivity, moisture management or flexibility is the priority, our solutions engineering team can identify and test adhesives that keep products performing—and patients comfortable.
Let’s create what’s next in wearable technology and medical care. Contact us today to start building your custom adhesive solution.