
Silicone elastomers are essential materials in modern engineering, providing flexibility, durability and high-performance capabilities across various industries. Their compressibility, combined...

Key Points:
A Sur-Seal Solutions Engineer weighs in on this critical topic: “Based on my knowledge and the years of work I have been involved in with HVAC engineers at the ground level, the UL flammability ratings required have always been a major topic of discussion and some of the toughest challenges I have faced.”
With that in mind, this guide will act as a resource to help you navigate many of the most pressing challenges surrounding UL flammability ratings and requirements.
Before we get into different flammability ratings, it’s essential to highlight the difference between flame retardancy and flame retardant.
Flame retardancy is a chemical that’s used in materials. It also measures what happens to a material when exposed to flame. It’s easy to confuse the two, so understanding how these terms differ will save you some headaches.
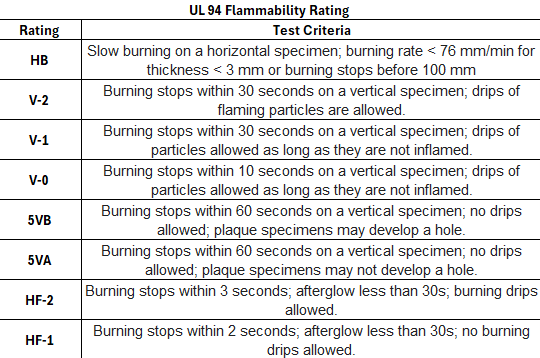
HVAC applications have multiple flame resistance (FR) ratings, but the most common are UL94 and UL723/ASTM E84. The main UL94 ratings are listed below from lowest (least flame-retardant) to highest (most flame-retardant):
There are also two other classifications common in the HVAC industry that apply to low-density foam materials:
The rating is often needed when the insulation or gasket is placed within the airstream.
UL94HB is rated for slow-burning specimens, while UL94HF-1 and UL94HF-2-rated materials are used to suppress flames.
UL94V-rated materials are most common in HVAC applications. UL94V variants have unique properties. UL94V-1 and UL94V-2 are rated to stop flames from burning within 30 seconds, but UL94V-2 allows flaming specimens to drip. UL94V-0 materials are specified to stop flames within 10 seconds.
In most cases, customers will provide you with the flammability rating they need to meet in a spec sheet.
Geographical locations differ in their rules and regulations. Some locations, like Chicago and the United Kingdom, have strict requirements because of past fire incidents.
Building codes and regulations often determine the flammability ratings required for indoor HVAC units, while outdoor units may have more flexibility.
A material with a high flammability level will have a higher cost to match it. UL94V-0 is the most expensive due to its impressive flame retardancy, while UL94HF-1 and UL94HF-2 cost slightly less. UL94HB is the least expensive of the common material ratings.
COST-EFFECTIVE TIP: One solution is to avoid using flame-retardant chemicals altogether, as they can drive costs up. Instead, use intrinsically flame-resistant materials.
Finding the proper flammability rating for your needs should be your priority, but it’s never a bad idea to look for opportunities to reduce costs.

When choosing the right flammability-rated materials, ask yourself these questions:
DECISION-MAKING TIP: The most important element to consider is the material’s application and function. Once you identify this, you can find where the flame-resistant material is used on the device and ask follow-up questions (like those listed above).
There are also more situational variables based on a product’s design that can reduce costs. For example, if you have a metal flame-retardant box with flame-retardant foam on the inside, you can substitute that insulating material for standard foam. Having two layers of flame resistance might be a good idea on paper, but realistically, it can be a waste of money because the flames would never reach inside the box.
Knowing your application’s design is invaluable for making the right material decision regarding flammability ratings.
With all the different UL flammability ratings and materials available in the HVAC market, finding the right fit that meets all the desired requirements and characteristics can be daunting. By focusing on what is most important and ensuring you meet the allotted spec based on industry regulations, we can find the material to meet your needs.
When creating products in the HVAC industry, you must be aware of many flame-resistance standards and regulations. Units often feature multiple material types, fluids such as oil and refrigerant, and flammable paint types.
These numerous flame hazards are why making the right fire-resistance choice is so important. It’s crucial to familiarize yourself with UL flame standards, including the outside factors to consider and questions to ask about them. These parts of the decision-making process can mean the difference between a functional product and a hazard.
Use this guide to inform your decision when selecting a flame-resistant foam, fabric, or other material for your next HVAC application. With the proper precautions and knowledge base, you can create products that can withstand the heat.
Need help with your HVAC application’s flame-resistant materials selection? Let’s talk! Contact us today.
Interested in learning more about our services? Explore the following: